Introduction
Fan balancing is one of the most sought-after procedures in equipment maintenance. This is due to the high sensitivity of fans to imbalance; even the slightest deviation can lead to significant vibrations. Imbalance occurs when there is a misalignment between the geometric center of the shaft and the center of mass. The higher the fan’s rotational speed, the more precise the balancing needs to be.
Causes and Consequences of Fan Imbalance
The most common causes of fan imbalance include:
- Abrasive wear on fan blades
- Dirt accumulation on fan blades
- Loose assembly, misalignment of the impeller relative to the hub
- Temperature fluctuations in the fan housing or on the shaft
- Loss of balancing weight
- Blade deformation
Operating an imbalanced fan results in vibrations that are hazardous to the overall structure. This leads not only to increased energy consumption but also to premature failure of bearings (either shaft or supporting structures) and unplanned downtime.
Conversely, a well-balanced fan:
- Makes the equipment more efficient
- Reduces stress on the equipment
- Extends the lifespan of your bearings
- Makes the fan operation quieter
Therefore, whether you are dealing with a new fan or maintaining/repairing an old one, neglecting the fan balancing stage is not recommended.
Important! Fan imbalance is the most common cause of increased vibration. However, there are other causes as well: structural failures or changes, large clearances, issues with belt drives, misalignments, cracks in rotors, and faulty bearings. Therefore, it’s crucial that experienced vibration diagnostic specialists determine the cause of increased vibration.
Specialist’s Comment
As experience shows, people seek balancing services whenever there’s an increase in vibration. However, balancing is the final step in reducing vibration. Before proceeding to it, a vibration diagnostic of the equipment’s condition must be conducted. All deficiencies, such as defects in coupling connections, lack of shaft alignment, or lack of rigidity in the support system, should be identified and removed. Only then should you proceed to the balancing stage, if it’s still relevant. For instance, a recent client needed a fan balancing for a dryer. Our vibration measurements, particularly the vibration velocity spectrum, indicated the presence of mechanical looseness. Further inspection revealed damage to the fan’s support system attachment to the foundation. After securing the supports to the foundation and re-diagnosing, the residual imbalance was within acceptable limits. Consequently, balancing was no longer necessary. These defects also prevent balancing. Balancing is only carried out on technically sound machines.
How Fan Balancing is Performed
Our specialists usually perform fan balancing (either the impeller or the fan wheel) on-site using the fan’s own bearings. This allows for maximum precision and speed without disassembly, thus avoiding unnecessary interference with the equipment structure.
In our fan balancing work, we always aim to achieve the lowest residual imbalance and adhere to balancing accuracy in accordance with ISO 1940-1-2007 for the respective equipment class. For this, we use a portable balancing device, the vibration analyzer Balanset-1A.
Steps Involved:
The balancing process consists of several stages. The number of sensors and their placement may be determined by the manufacturer. General guidelines recommend placing sensors on the bearings of the fan shaft and on the housing. If this is not possible due to technical reasons or design features, they are placed in locations with the shortest connection between them and the bearings.
- Install the vibration sensors perpendicular to the rotor rotation axis.
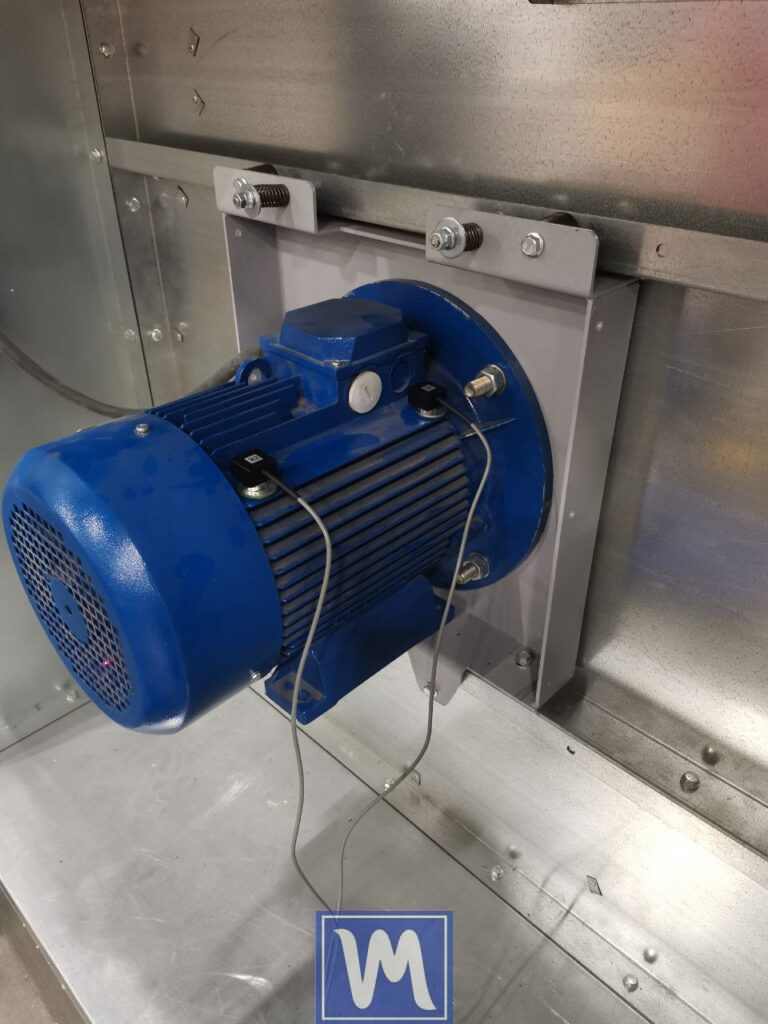

a two-plane dynamic balancing process for an industrial radial fan. The procedure aims to eliminate vibration and imbalance in the fan’s impeller. Balanset-1 Vibromera
- Mount the tachometer on the magnetic stand.
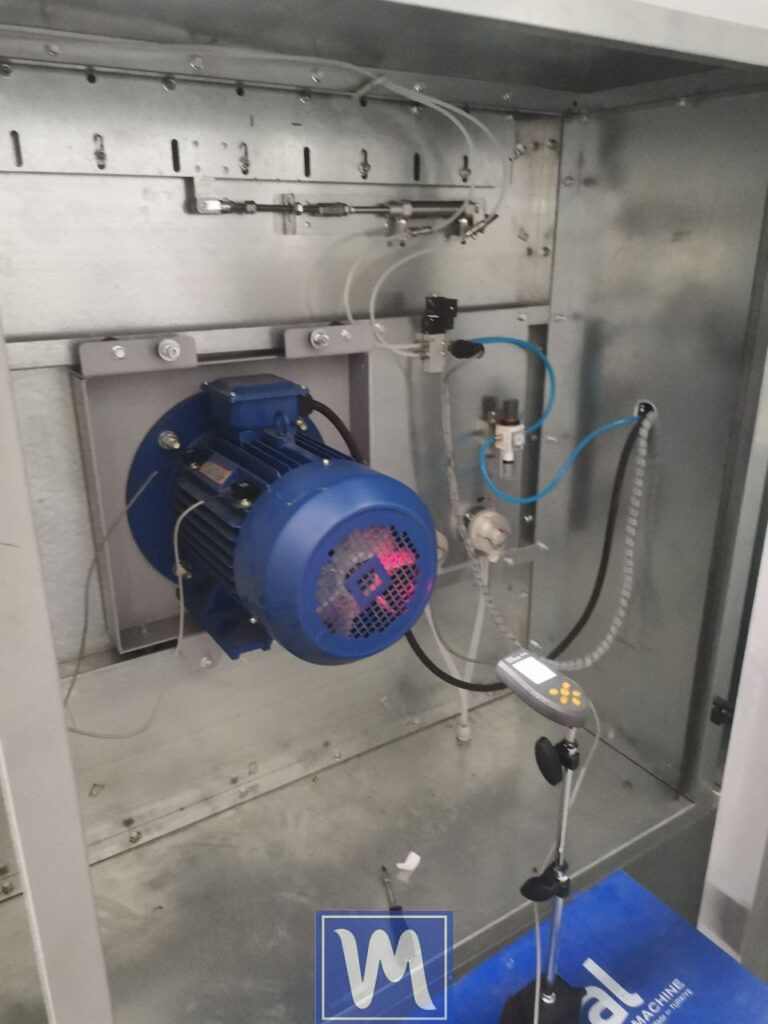

a two-plane dynamic balancing process for an industrial radial fan. The procedure aims to eliminate vibration and imbalance in the fan’s impeller. Balanset-1 Vibromera
- Stick reflective tape on the pulley and point the RPM sensor toward the tape.
- Connect the sensors to the device and the device to the laptop.
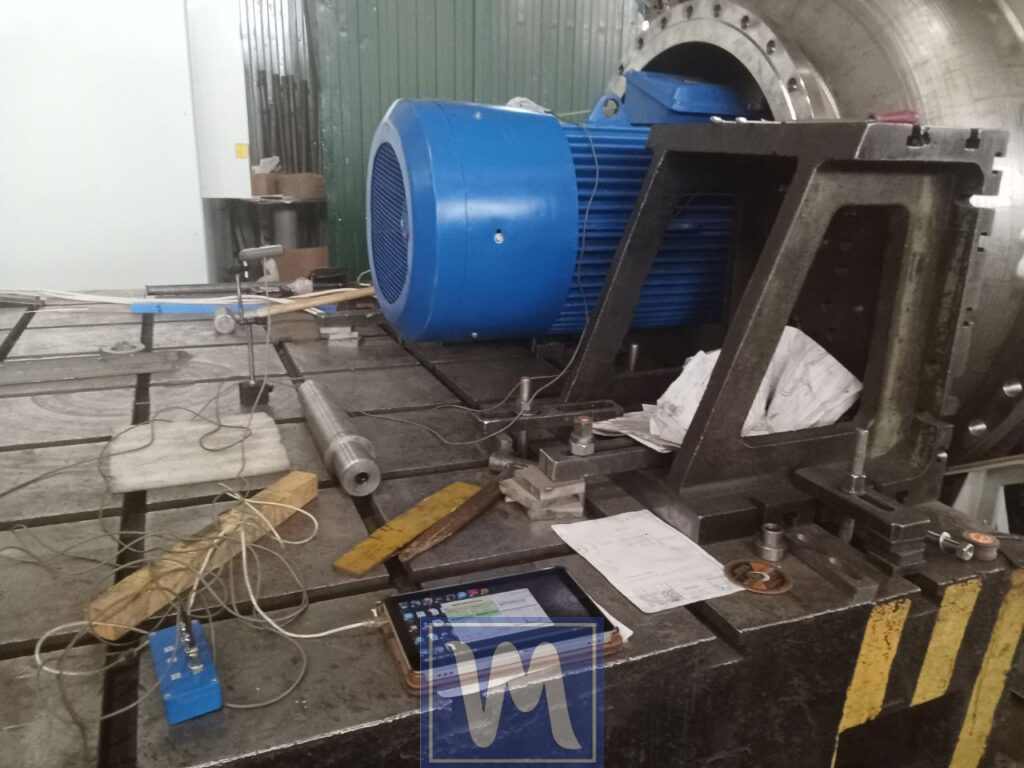

a two-plane dynamic balancing process for an industrial radial fan. The procedure aims to eliminate vibration and imbalance in the fan’s impeller. Balanset-1 Vibromera
- Start the program.
- Select two-plane balancing.
Software for the Balanset-1A portable balancing instrument and vibration analyser. Main Menu Screen.
- Enter the name of the rotor and its location.
- Weigh the test weight and record the weight and radius of installation.
Software for the Balanset-1A portable balancing instrument and vibration analyser. Setting up dynamic balancing.
- Start rotating the rotor and measure the initial vibration level.
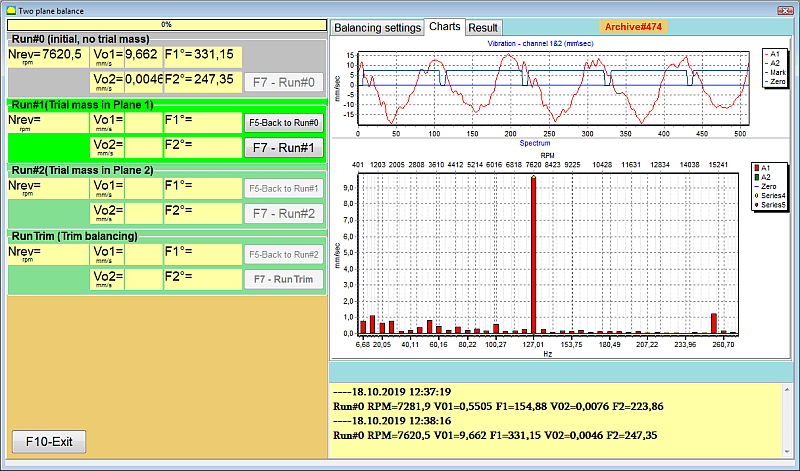
Software for Balanset-1A portable balancer and vibration analyser. Two plane balancing window. Original vibration
- Install the test weight in the first plane.
- Start rotating the rotor and take a second measurement.
- Verify that the vibration or phase has changed by at least 20%.
- Remove the test weight from the first plane and place it on the second plane.
- Start rotating the rotor and take a third measurement.
- The program will show how much weight and at what angle to place in the first and second planes.
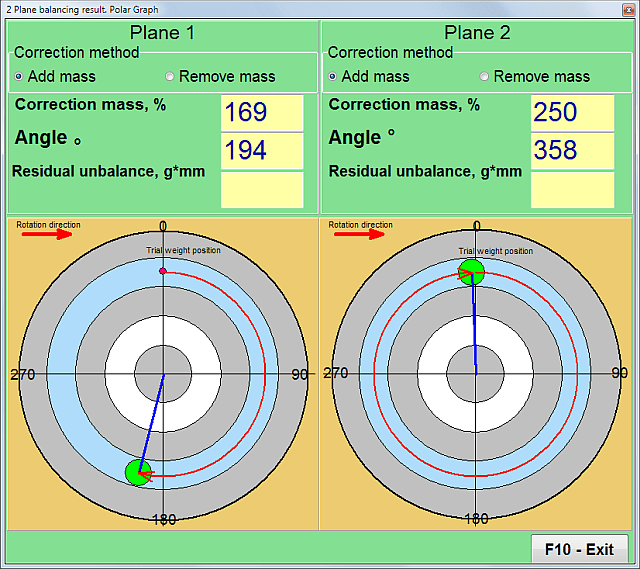
Software for the Balanset-1A portable balancing instrument and vibration analyser. Dual plane balancing. Polar chart .
- Remove the test weight.
- Weigh the mass of the correction weight.
- Weld the correction weights.
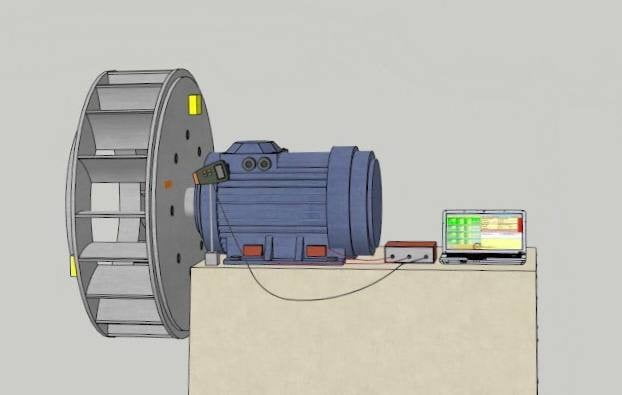
portable dynamic balancer, vibration analyzer “Balanset-1A”
- Start rotating the rotor and check that the balancing was successful.
- If the software prompts you to add some more weight, add it and check the balance again.
By following this sequence, we ensure the highest level of precision in fan balancing, contributing to the long-term efficiency and reliability of your industrial equipment.






